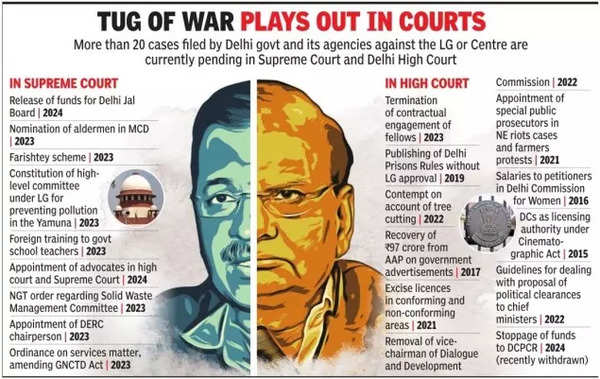
The ruling addresses a longstanding dispute over the extent of the Delhi government's influence over municipal appointments. Previously, the Delhi government argued that its assistance was necessary for alderman nominations, reflecting the party's broader contention that it should have more control over municipal functions. However, the Supreme Court's decision reinforces the LG's independence in making such appointments, potentially impacting the administrative balance within the MCD.
The case highlights the intricate relationship between central and local authorities in Delhi, where governance issues often lead to legal challenges. The Supreme Court's verdict comes amidst ongoing debates about the distribution of powers between the Delhi government and the LG, a conflict that has been a central issue in local politics. The judgment emphasizes the LG's role as a key figure in municipal administration, potentially reshaping the future interactions between Delhi's elected government and the MCD.
This decision follows a series of legal battles and political controversies involving the Aam Aadmi Party (AAP) government and the LG. The AAP, which has been critical of the LG's role and its impact on the Delhi government's operations, faces a significant setback with this ruling. The party's leaders have previously accused the central government of undermining their authority, and this judgment could intensify their criticism of the central administration.
In the broader context, the ruling could influence how other states and union territories approach their administrative frameworks, particularly in regions where similar disputes between local and central authorities exist. The Supreme Court's stance reinforces the LG's authority in Delhi, setting a precedent that might affect governance structures elsewhere.
The implications of this decision extend beyond political friction, impacting the functionality of the MCD. The aldermen, nominated by the LG, will play a role in the municipal corporation's decision-making processes, potentially altering the dynamics within the MCD. The ruling underscores the need for clarity in the delineation of powers and responsibilities between different levels of government, especially in complex administrative environments.
Overall, the Supreme Court's ruling underscores the importance of understanding the balance of power in governance. The decision reflects ongoing tensions and legal interpretations regarding the roles of different governmental bodies, shaping the future of Delhi's municipal administration and potentially influencing similar administrative disputes across India.
